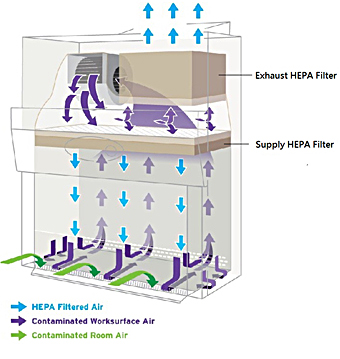
 |
Air flow pattern of the Nuaire Biosafety
Cabinet commonly used on campus |
|
Biosafety cabinets are designed to house work involving biological materials to prevent exposure of the operator to the biological material, avoid contamination of the biological material and to curb the spread of the biological material beyond the confines of the cabinet. However, these protective measures will only be effective if the cabinets are used correctly. Here are some tips:
How does the biosafety cabinet work?
The incoming room air current (green) prevents aerosols inside the cabinet from coming out causing an exposure of the worker. Together with the contaminated work surface air (purple), the room air (green) goes up through the back of the cabinet to the top. Thirty percent (30%) of the contaminated air will be exhausted through a HEPA filter and the remaining 70% of the contaminated air will be re-circulated through the supply HEPA filter. This 70% filtered/sterilized air (blue) is blown by the blower down onto the work surface, thus preventing the work area from contamination. After going through the work surface, the potentially contaminated air mixes with the incoming room air and goes up to the top of the cabinet again.
Proper Operating Procedures
- Always preload biosafety cabinet with all necessary instruments and materials.
- Turn on biosafety cabinet and let it run for about 15 minutes.
- When working with the cabinet, operator's arm should enter straight into the cabinet and perform work in a methodical and steady manner.
- Upon completion of work, decontaminate all items before taking them out of the cabinet.
- Wipe down the internal surfaces of the cabinet with an appropriate disinfectant.
- Let cabinet run for about 15 minutes prior to turning it off.
- Review user's manual for additional instructions.
Safe Operation
- Arms should always enter straight into cabinet. Do not sweep across the cabinet.
- Put materials well within the cabinet — never on top of front or back air grill.
- Put disposal pan inside cabinet.
- Avoid disrupting the laminar air flow.
- Decontaminate materials before removing them from the cabinet.
- Biosafety cabinets are not designed for handling large amount of chemicals.
- May work with non-volatile toxic chemicals or low-level radioactive materials.
- Can only work with small amount of volatile chemicals.
- Arrange for annual calibration and certification.
Cautions
- Chemical materials may damage HEPA filter.
- Volatile chemicals cannot not be removed by HEPA filter.
- Biosafety cabinets are not sparkproof — flammable chemical used inside the cabinet may result in fire or explosion.
- Use of Bunsen burners or other flames inside the cabinet should be avoided.
References
3rd Edition, Primary Containment for Biohazards: Selection, Installation and Use of Biological Safety Cabinets. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Institutes of Health, September 2007.
 |